Their unique climate with high temperatures, humidity, and precipitation promotes high primary productivity, which offsets high respiration, resulting in these ecosystems being one of the largest carbon sinks on Earth, storing about 25% of all terrestrial carbon on the planet.
However, climate experts have demonstrated that tropical forests are experiencing disturbances to their hydrological cycle in the form of longer drought periods and more intense precipitation, which research shows can impact soil nutrient cycling and may decrease soil carbon storage as a result. Now a research team led by EESA scientists Stephany Chacon and Nicholas Bouskill conducted a study published in Soil Biology and Biogeochemistry to investigate how soil drying impacts soil microbial communities, which largely govern soil carbon storage through their ability to decompose soil organic matter (carbon). Their findings suggest that how soil microbes respond to drought is dependent on a given region’s climate history and soil fertility.
“The emergence of microbial traits, which dictate resilience to disturbance, is dependent upon long-term exposure to stress,” Bouskill explained, “and we might expect that drier regions are more resilient to soil drying. This is basically what we saw, but also noted that nutrient availability also imparted strong resistance to stress.”
An area’s climate history, which can influence a microbial community’s traits and functions, can impact how soil microbes respond to environmental disturbance such as wildfire or flooding. The researchers studied how changing precipitation levels among four sites with varying climate histories and soil fertility impacted the evolutionary development and community composition of tropical soil microbes throughout Panama over the course of 18 months. To simulate drought conditions, they used plastic shelters to prevent precipitation from directly entering the soils.
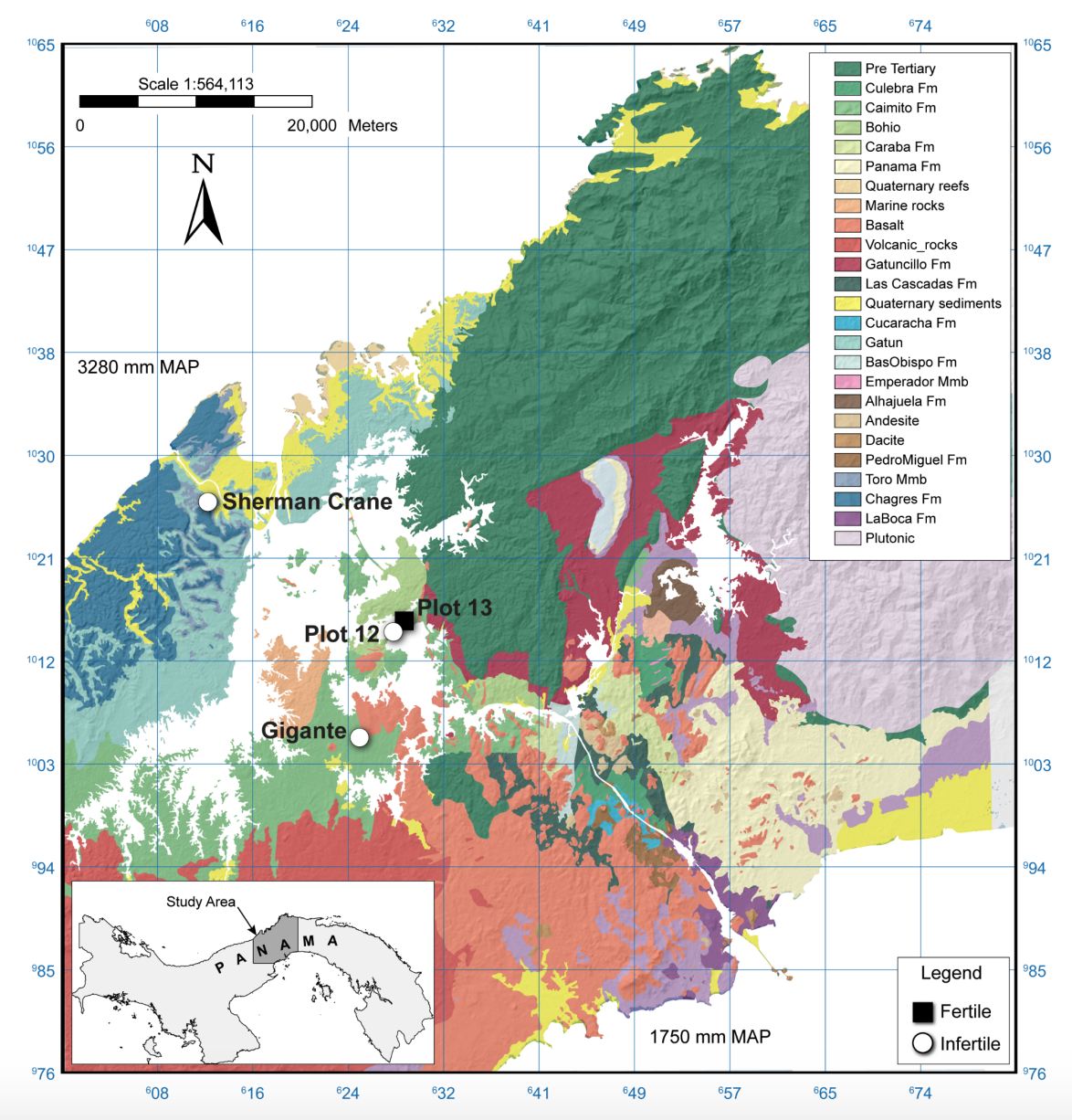
The team found that a “drought microbiome” developed in less fertile soils across different sites receiving a lower average annual precipitation, showing more similarities in composition and structure towards one another despite being from different locations. As the team reduced precipitation, they found that, in sites with higher average annual precipitation, microbial community makeup changed to resemble communities from areas with a history of receiving lower precipitation.
These findings demonstrate that, as climate changes and drought occurs in tropical forests, microbial communities’ response to drying soils might be influenced by climate history and soil fertility. Since microbial communities are sensitive to change on even the smallest of scales, understanding how they will respond to larger changes like drought is essential to predicting their activity and in turn soil carbon storage in a changing climate.


